350
YEARS
OF
SCIENCE
51
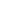
© Archives de l'Aacdémie des sciences
Pierre (1859-1906) et Marie (1867-1934) Curie
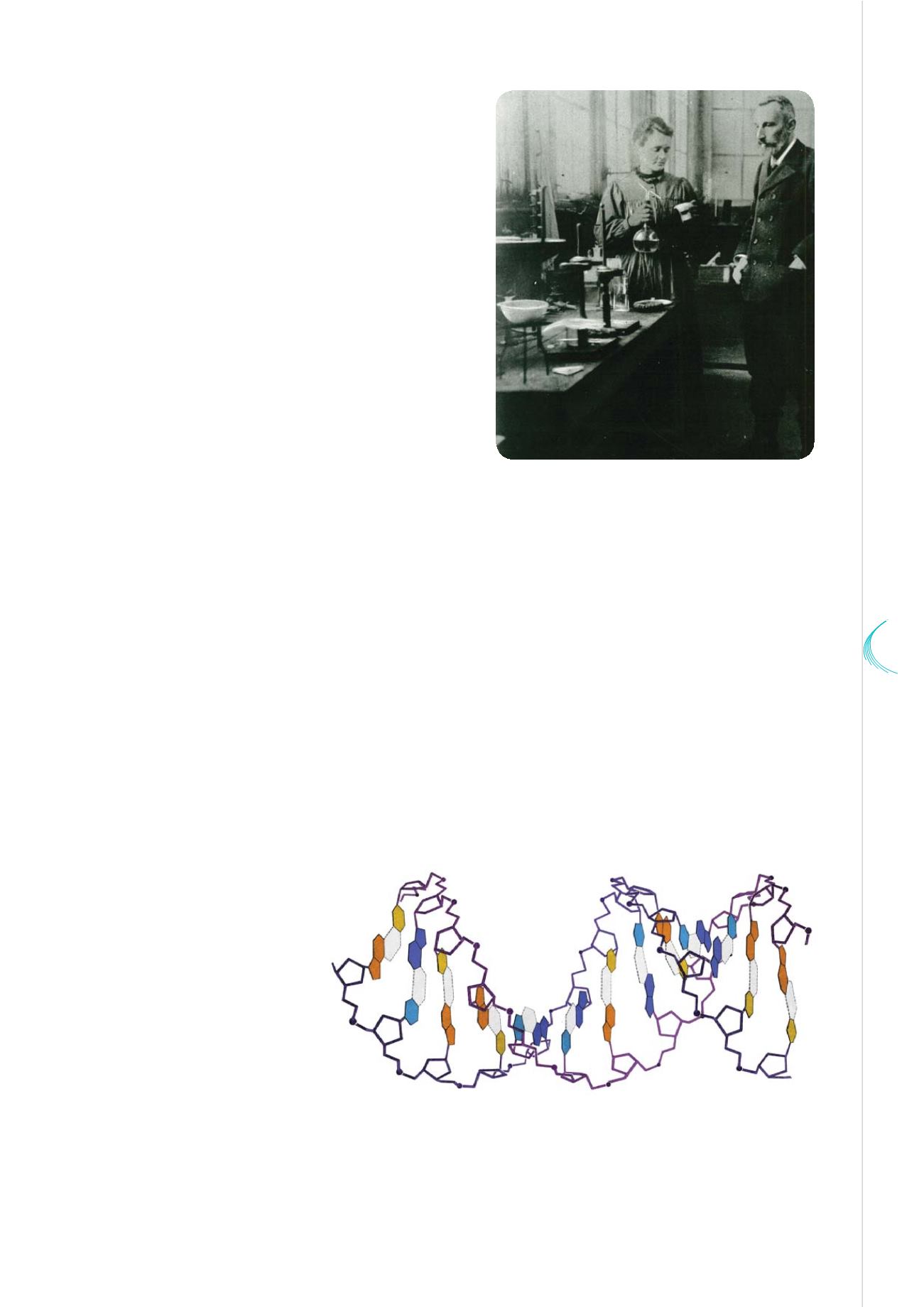
The Watson-Crick model of the structure of DNA
© Photo Researchers, Inc - Alamy
In the 20
th
century, chemistry diversifies
With quantum theories developing and
characterization techniques improving in the
course of the 20
th
Century, chemistry experienced
a rapid evolution. It conspicuously deepened
and diversified at the same time. New disciplines
appeared: catalysis, solid state chemistry,
organometallic
chemistry,
computational
chemistry, physical chemistry, biochemistry,
geochemistry, etc. The discovery of radioactive
elements - polonium and radium - by Pierre
and Marie Curie marked the beginning of
radiochemistry, with all its impacts on the fields of
medicine, energy, and even weapons.
The quantum description of the electrons shed new light on their behaviours within matter. It became
possible to provide a quantitative description of chemical bonding and of the electronic properties of
molecules (Pauling, 1954 Nobel Prize; Ken'ichi Fukui and Hoffmann, 1981 Nobel Prize). Theoretical
chemistry would play an ever-increasing role. It became predictive and would be rewarded with two Nobel
Prizes, the first one being for quantum methods (Pople and Kohn, 1998) and the other one for multiscale
methods, that allow the behaviour of a population of several hundred thousand atoms to be modelled
(Karplus, Levitt and Warshell, 2013).
At the same time, the analysis tools and characterization techniques - X-ray diffraction, NMR, electron
microscopy, scanning tunneling microscopy, etc. – provided a much finer picture of the structure of
matter. The determina-
tions of the structure of
insulin (Sanger, 1958 No-
bel Prize) and of the DNA
double helix (Watson and
Crick, 1962 Nobel Prize)
were most significant
examples of it.
With such new data,
chemical synthesis en-
countered considerable
developments. Chemists
became more skilled at
transforming matter to