37 38
58
La Lettre
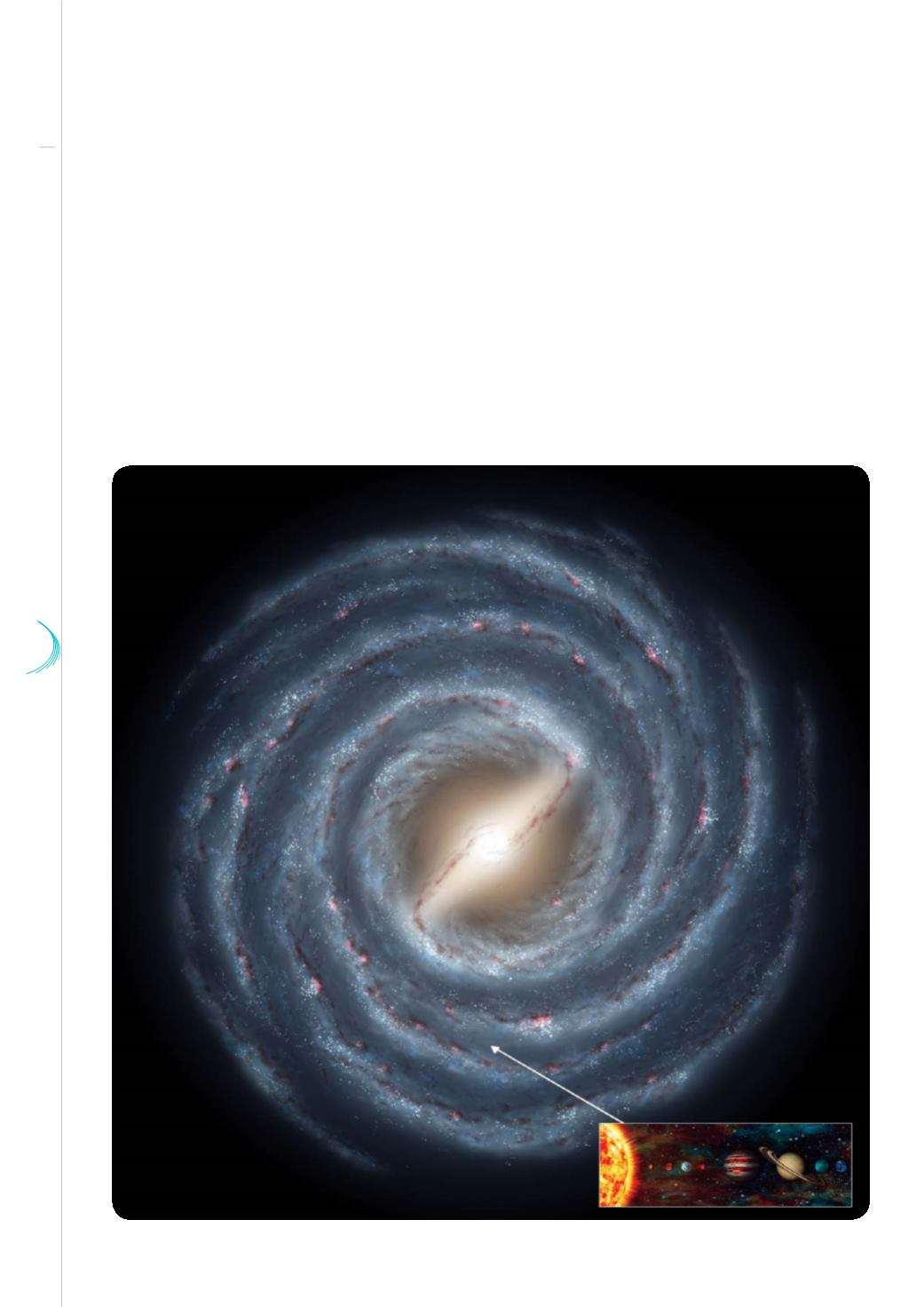
The sun inside the Milky Way (artist view)
© Caltech et NASA
Nuclear physics and the study of radioactivity (Becquerel, Rutherford, the Curie couple) would, between 1850
and 1950, provide the bases for an explanation of the origins of the elements. The sun then became a star like
the others, its energy deriving from reactions of nuclear fusion (Perrin, Eddington). Nucleosynthetis reactions
became known to occur within the stars which, at the end of their evolution, were acknowledged to enrich the
interstellar medium with heavier elements (Burbidge). The age of Earth was estimated, by means of natural
radioactivity counting techniques, at 1 and then 4 billion years during the first half of the 20
th
Century.
At the end of such progress, it has been established that the sun and its train of planets are in motion in
the Milky Way, our Galaxy, which comprises hundreds of billion stars more or less comparable to ours. The
Milky Way has become but a galaxy among hundreds of thousand others within the expanding Universe
(Shapley, Ross, Hubble).